Attentional Learn-able Pooling for Human Activity Recognition
Bappaditya Debnath, Mary O’Brien, Swagat Kumar and Ardhendu Behera
Department of Computer Science, Edge Hill University, United Kingdom
Abstract
Human activity/behaviour monitoring and recognition is a key for facilitating humans robot interaction, and allows robots for a better scheduling of future operations. It is challenging and often addressed at different levels, such as human activity classification, future activity prediction and monitoring of the on-going activities. The paper proposes a novel attention-based learn-able pooling mechanism for human activity classification from RGB videos. Recently, most of the best performing human activity recognition approaches are based on 3D skeleton positions. The 3D skeleton positions are not always available in videos captured using RGB cameras, which are widely used in robotics applications. RGB videos contain rich spatio-temporal information and processing them semantically is a difficult task. Moreover, accurately capturing spatial information and long-term temporal dependencies is the key to achieving high recognition accuracy. We use an existing Convolutional Neural Network for image recognition to extract video features which are then processed using our innovative application of attention mechanism to focus the network on features that are more important for discrimination. Afterwards, we use a novel learn-able pooling mechanism to extract activity-aware spatio-temporal cues for efficient activity recognition. The proposed pooling mechanism learns the structural information from hidden states of a bidirectional Long Short-Term Memory network via Fisher Vectors.
Attentional Learn-able Pooling
Our novel attention mechanism consists of two parts: 1) a sequential self-attention mechanism is used to selectively focus the high-level CNN representations on important temporal points. 2) The output of this sequential selfattention is fed into a bi-LSTM to capture the long-term temporal dependencies. We adapt the bi-LSTM to learn the structural information and similarities contained within its hidden states through Fisher Vectors (FVs). The FVs are based on a clustering mechanism that semantically groups information. By exploiting the LSTM hidden states, with learn-able FVs the network is able to take advantage of this information. The output of learn-able FVs is pooled using AAP to represent the number of states equalling the number of activity classes. The novel learn-able FVs with AAP replaces the customary Global Average Pooling (GAP).
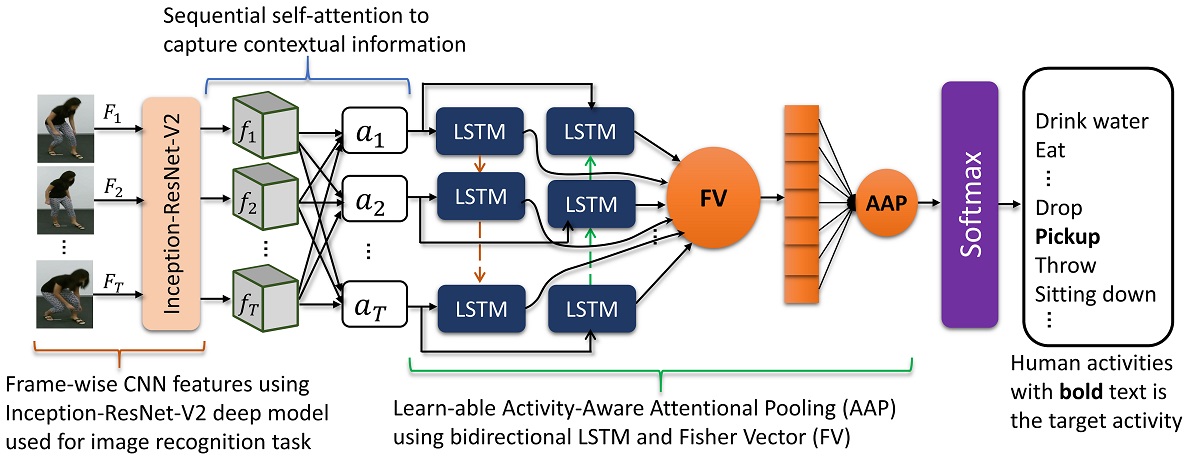 The proposed deep network consists of: 1) a pre-trained CNN (Inception-ResNet-V2) model used to extract frame-wise high-level CNN features from a given video consisting of T frames. 2) a sequential self-attention layer to capture the contextual information consisting important spatial and temporal knowledge. 3) Learn-able AAP consisting a bidirectional LSTM (bi-LSTM) and FV to learn the structural information and similarities by exploring the hidden states of the bi-LSTM.
The proposed deep network consists of: 1) a pre-trained CNN (Inception-ResNet-V2) model used to extract frame-wise high-level CNN features from a given video consisting of T frames. 2) a sequential self-attention layer to capture the contextual information consisting important spatial and temporal knowledge. 3) Learn-able AAP consisting a bidirectional LSTM (bi-LSTM) and FV to learn the structural information and similarities by exploring the hidden states of the bi-LSTM.
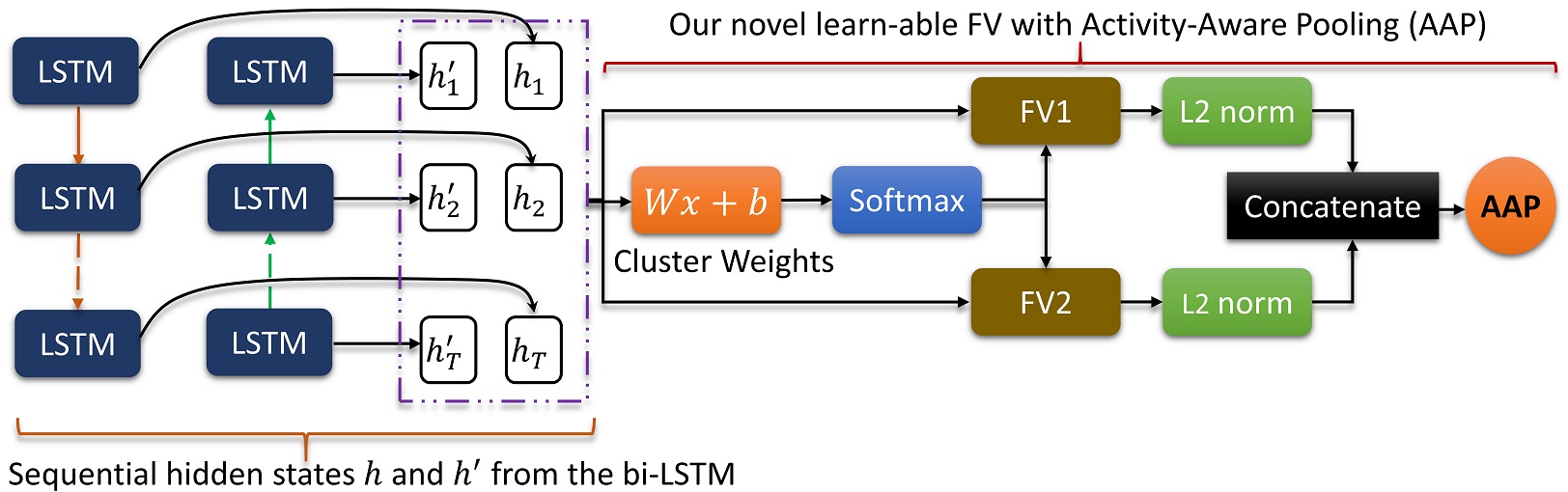 The details of the proposed learn-able FV pooling using a bidirectional LSTM (bi-LSTM): The structural information in hidden states of the bi-LSTM is learned through FV with AAP.
The details of the proposed learn-able FV pooling using a bidirectional LSTM (bi-LSTM): The structural information in hidden states of the bi-LSTM is learned through FV with AAP.
Paper
Bibtex
@inproceedings{debnath2021attentional,
title={Attentional Learn-able Pooling for Human Activity Recognition},
author={Debnath, Bappaditya and O'BRIEN, MARY and Kumar, Swagat and Behera, Ardhendu},
booktitle={IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA)},
year={2021},
organization={Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.}
}
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Research Investment Fund (RIF) at Edge Hill University, and UKIERI (CHARM) under grant DST UKIERI-2018-19-10. The GPU is kindly donated by the NVIDIA Corporation.